Martyn’s Law, also known as the Protect Duty, is a proposed legislation in the United Kingdom aimed at enhancing public safety by requiring owners and operators of publicly accessible locations to take steps to protect people from terrorist attacks. It is named in honour of Martyn Hett, one of the victims of the 2017 Manchester Arena bombing.
Pullout panels































Concertina styles

Why was Martyn’s Law introduced?
Martyn’s Law was introduced in response to the growing threat of terrorism and to ensure that venues are better prepared to respond to such incidents. It aims to establish a consistent and effective approach to security across a variety of public spaces, helping to prevent future attacks and minimize their impact.
What types of locations are affected by Martyn’s Law?
The law applies to a wide range of publicly accessible locations, including but not limited to:
- Concert halls and arenas
- Shopping centres
- Public squares and parks
- Sports stadiums
- Large entertainment venues
- Places of worship
- Educational institutions
Essentially, any place where large numbers of people gather and could potentially be targeted by terrorists.
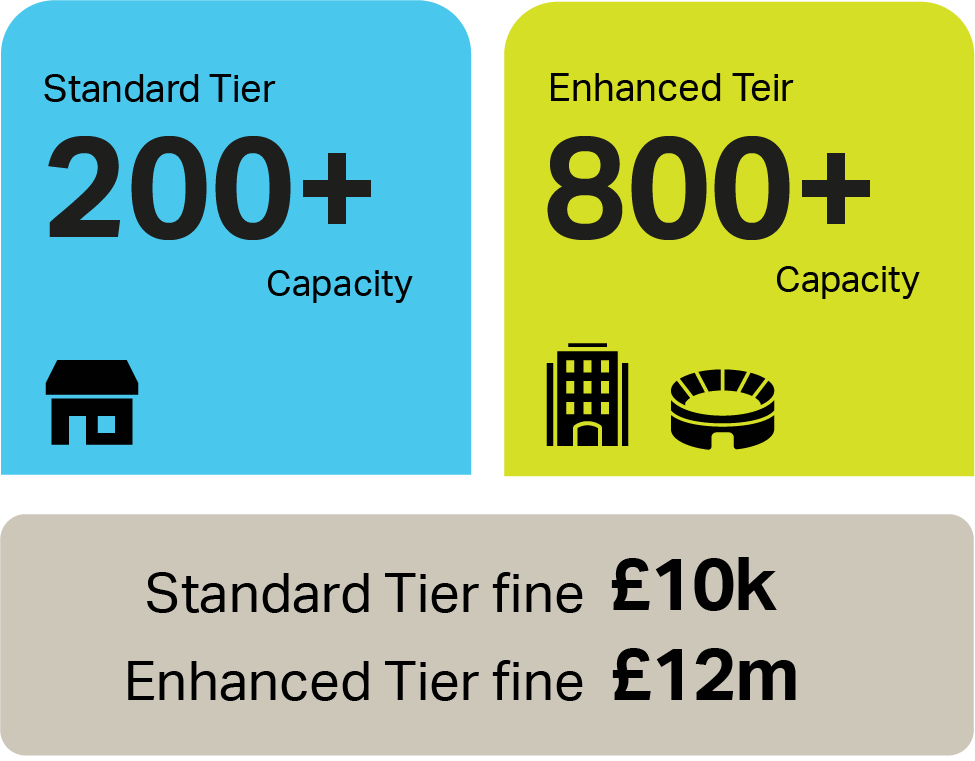
What will be the key requirements of Martyn’s Law for venue operators?
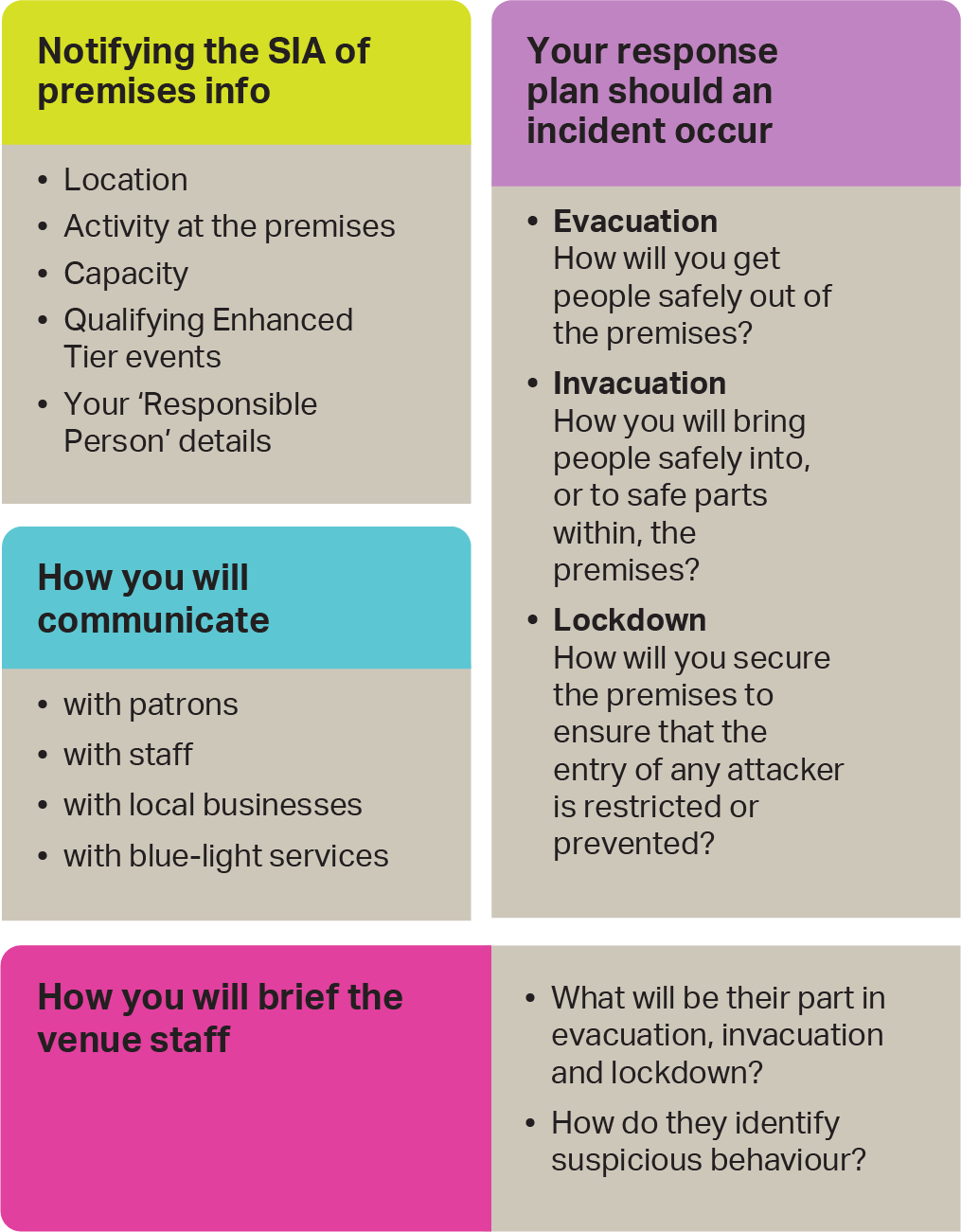
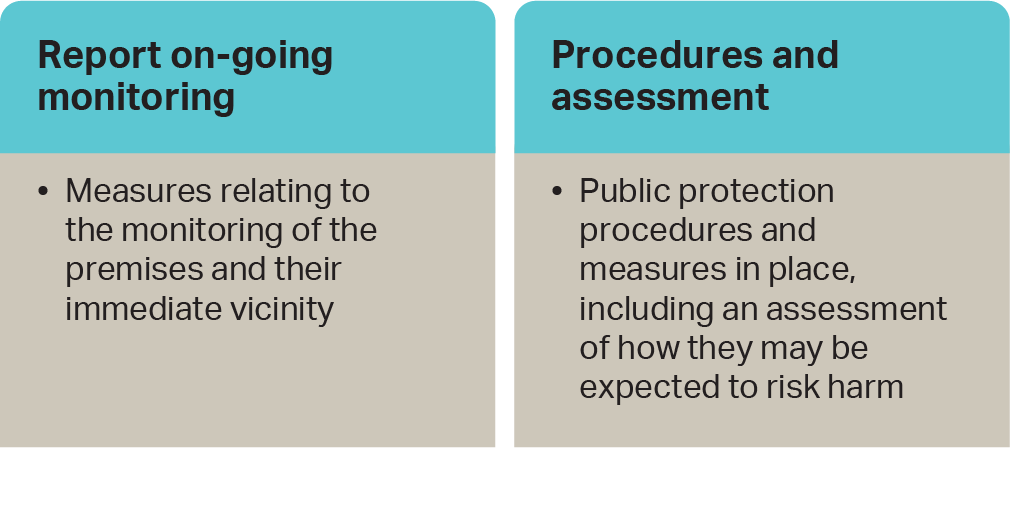
Risk Assessment: Conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats.
Mitigation Measures: Implementing appropriate and proportionate measures to reduce the risks identified, which may include physical security measures, staff training, and emergency response planning.
Training and Awareness: Ensuring that staff are adequately trained to recognize and respond to security threats.
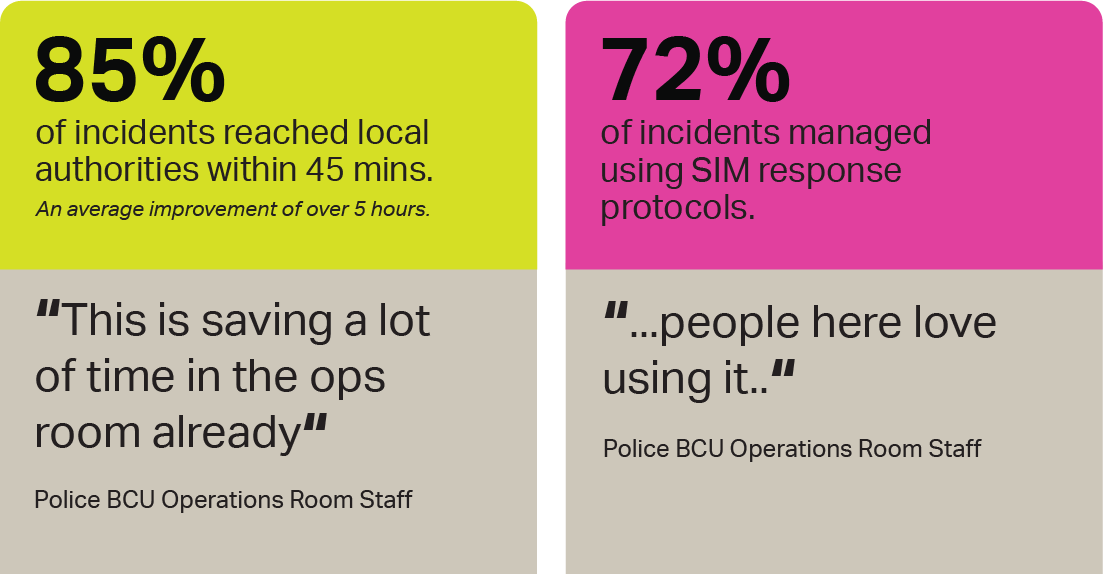
Collaboration: Working with local authorities, emergency services, and other stakeholders to enhance overall security and preparedness.
Information Sharing: Sharing relevant security information and intelligence with appropriate authorities and other operators.
How will compliance with Martyn’s Law be monitored and enforced?
Compliance with Martyn’s Law will be monitored and enforced by designated regulatory bodies, which may include local authorities and other government agencies. These bodies will have the authority to conduct inspections, review risk assessments and mitigation plans, and take enforcement action if necessary, including issuing fines or other penalties for non-compliance.
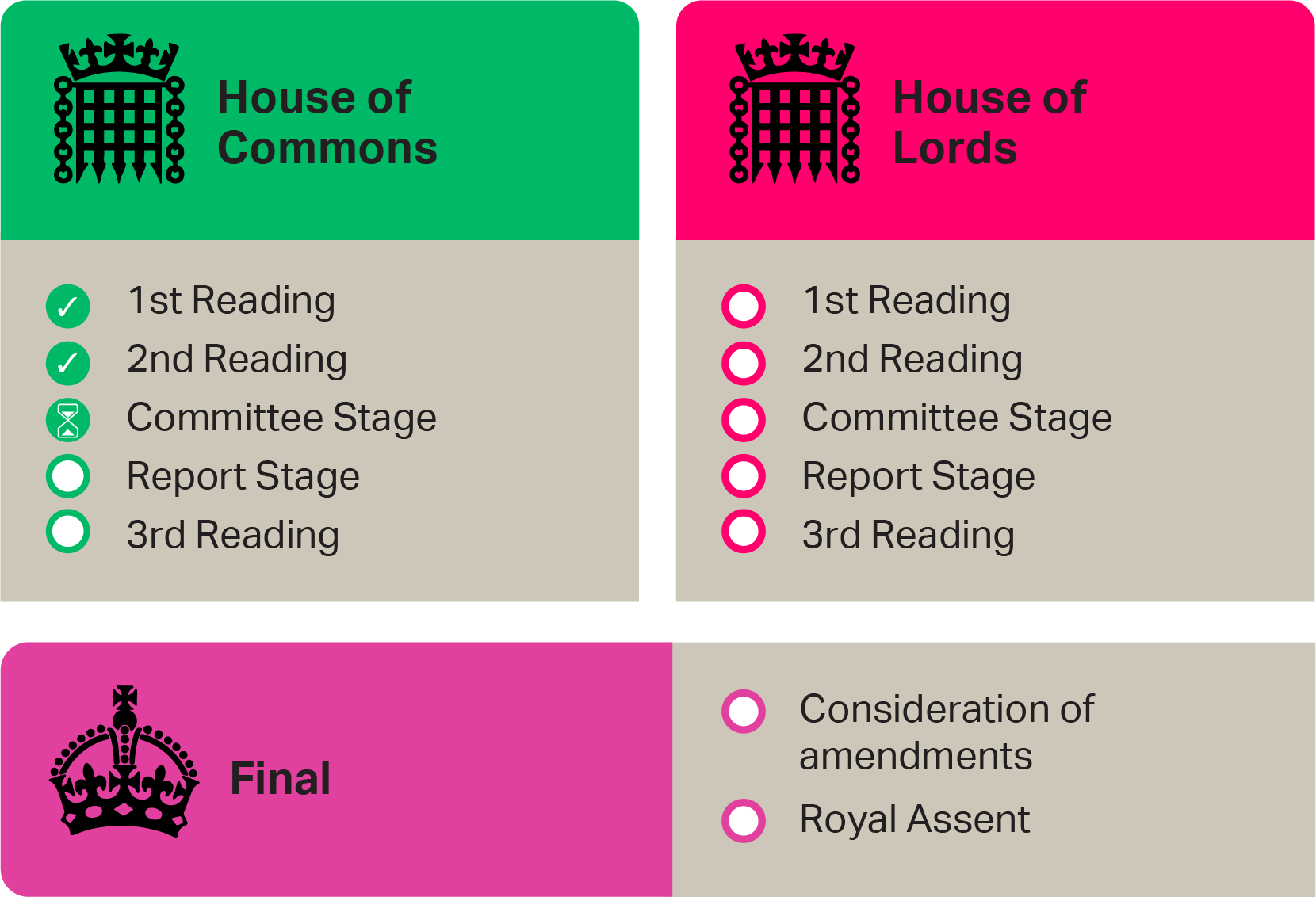
When is Martyn’s Law expected to come into effect?
The exact timeline for the implementation of Martyn’s Law is still being determined, as it is subject to the legislative process. However, the UK government has expressed a strong commitment to moving forward with the legislation, and it is anticipated to be enacted in the near future.

Sign-up panels










Sign-up for newsletter



Charts


Premises types












Charts





