Martyn’s Law, also known as the Protect Duty, is legislation in the United Kingdom aimed at enhancing public safety by requiring owners and operators of publicly accessible locations to take steps to protect people from terrorist attacks. It is named in honour of Martyn Hett, one of the victims of the 2017 Manchester Arena bombing.
Created for the most challenging uses.
SIM products are researched, developed and tested in partnership with the Met Police, Local Authorities and London's Violence Reduction Unit to manage incidents in London.

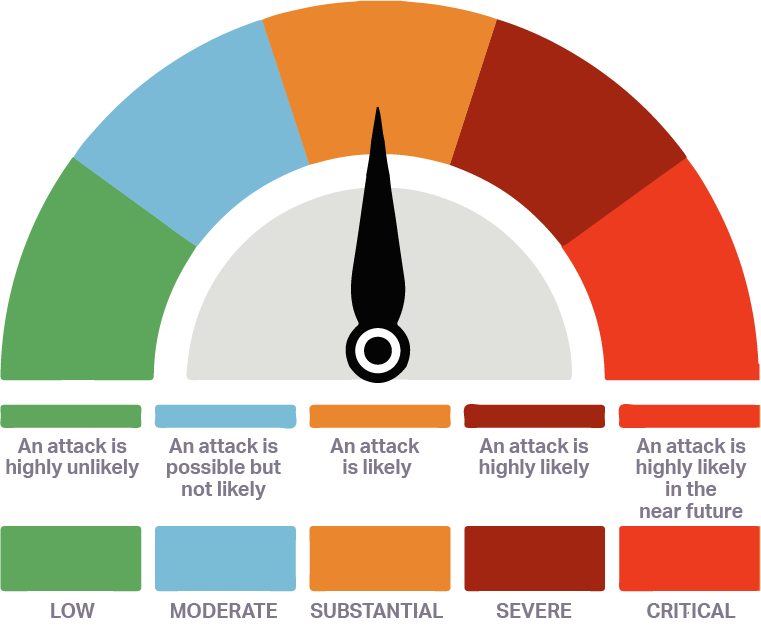
Current threat level - Substantial
FAQs
Why was Martyn’s Law introduced?
Martyn’s Law was introduced in response to the growing threat of terrorism and to ensure that venues are better prepared to respond to such incidents. It aims to establish a consistent and effective approach to security across a variety of public spaces, helping to prevent future attacks and minimize their impact.
What types of locations are affected by Martyn’s Law?
The law applies to a wide range of publicly accessible locations, including but not limited to:
- Concert halls and arenas
- Shopping centres
- Public squares and parks
- Sports stadiums
- Large entertainment venues
- Places of worship
- Educational institutions
Essentially, any place where large numbers of people gather and could potentially be targeted by terrorists.
What will be the key requirements of Martyn’s Law for venue operators?
Risk Assessment: Conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats.
Mitigation Measures: Implementing appropriate and proportionate measures to reduce the risks identified, which may include physical security measures, staff training, and emergency response planning.
Training and Awareness: Ensuring that staff are adequately trained to recognize and respond to security threats.
Collaboration: Working with local authorities, emergency services, and other stakeholders to enhance overall security and preparedness.
Information Sharing: Sharing relevant security information and intelligence with appropriate authorities and other operators.
How will compliance with Martyn’s Law be monitored and enforced?
Compliance with Martyn’s Law will be monitored and enforced by designated regulatory bodies, which may include local authorities and other government agencies. These bodies will have the authority to conduct inspections, review risk assessments and mitigation plans, and take enforcement action if necessary, including issuing fines or other penalties for non-compliance.
When is Martyn’s Law expected to come into effect?
The exact timeline for the implementation of Martyn’s Law is still being determined, as it is subject to the legislative process. However, the UK government has expressed a strong commitment to moving forward with the legislation, and it is anticipated to be enacted in the near future.

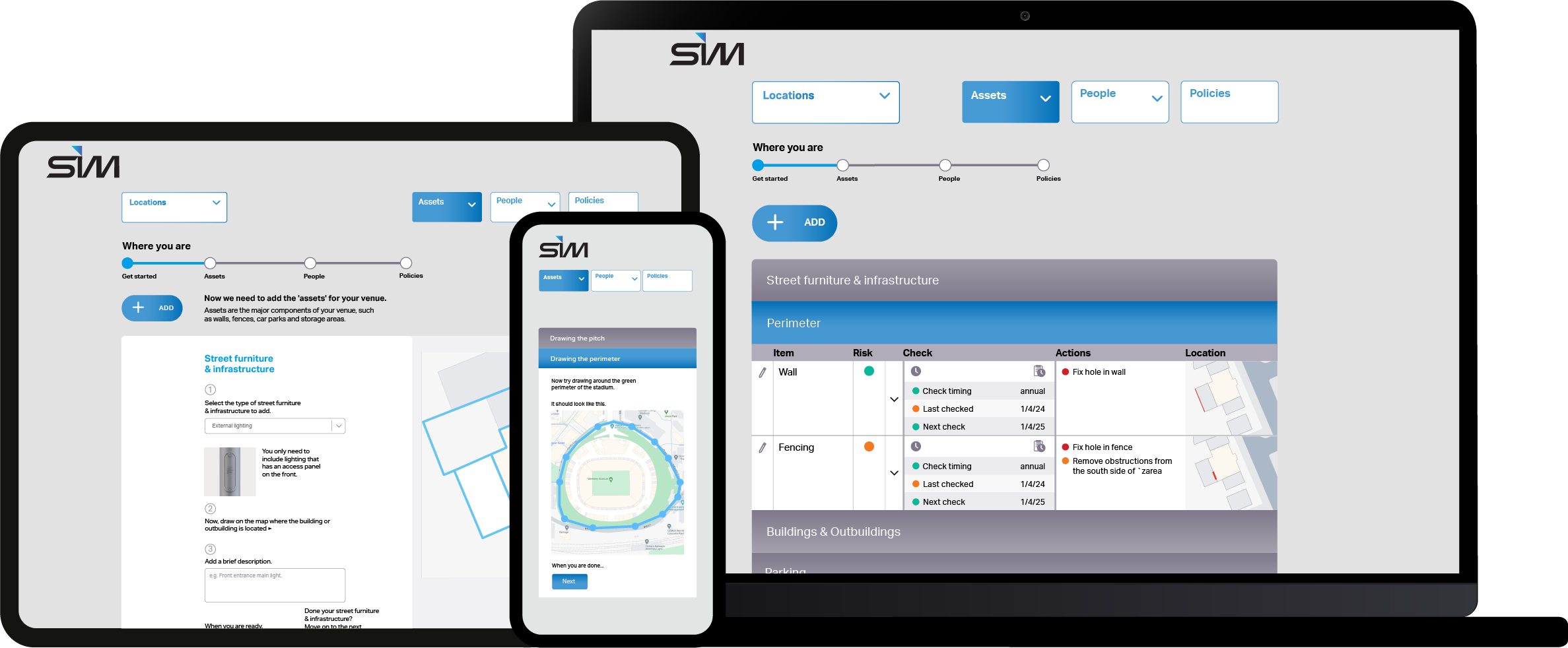
SIM Martyn's Law Manager is an easy-to-use digital tool for venue managers to ensure they protect their patrons and premises against terrorist attacks.
Created for the most challenging uses.
SIM products are researched, developed and tested in partnership with the Met Police, Local Authorities and London's Violence Reduction Unit to manage incidents in London.

What is Martyn’s Law?
The Terrorism (Protection of premises) Bill or Martyn's Law, will improve protective security and organisational preparedness across the UK by mandating, for the first time, those responsible for premises and events to consider the terrorist risk and how they would respond to an attack.


Martyn's Law passed into law on the 3rd April 2025.
How will it be enforced?
An inspection regime will be put in place by the UK Government, and the regulator, the Security Industry Authority (SIA), will have powers of entry into any qualifying location. Sanctions can range from a fine or closure of the location to prosecution. However, the priority is for the Government to give venues the straightforward guidance and simple tools they need to help prevent terror attacks and save lives.
Martyn's Law Timeline
May 22, 2017 - Manchester Arena Bombing
Manchester Arena Bombing: A terrorist attack during an Ariana Grande concert at Manchester Arena results in 22 deaths, including Martyn Hett, and hundreds of injuries.
2018 - The Kerslake Report published
The Kerslake Report is an independent review of the emergency response to the Manchester Arena bombing.
2018 - Figen Murray’s Advocacy Begins
Figen Murray, the mother of Martyn Hett, starts campaigning for stronger security measures at public venues to prevent similar tragedies.
2019 - The Manchester Arena Inquiry
The inquiry was established to provide a thorough and transparent investigation into the events leading up to, during, and after the attack to identify what went wrong, what could have been done differently, and how future responses to similar incidents can be improved.
2019 - Martyn’s Law Concept Introduced:
Figen Murray formally introduces the idea of Martyn’s Law, advocating for mandatory security measures at venues to protect the public from terrorism. The campaign begins to gain public and political attention.
Early 2021 - Government Consultation
The UK government conducts a consultation process to gather input on the proposed Martyn’s Law, engaging with stakeholders, including venue operators, security experts, and the public.
December 2021 - Government Commitment
The UK government officially commits to introducing Martyn’s Law, incorporating it into its legislative agenda with plans to bring the law before Parliament.
2022 - Legislative Development
The government works on drafting the law, refining its details based on the consultation process, and preparing it for implementation.
February 2024 - March 2024 - Consultation Period
The Government have launched a Martyn's Law consultation to ensure the public can share their views on these proposals for the Standard Tier.
July 2024 - King Charles Speech
King Charles' speech to both houses of Parliament addressed the adoption of anti-terrorism measures; "Measures will be introduced to improve the safety and security of public venues and help keep the British public safe from terrorism - the Terrorism (Protection of Premises) Bill."
2024 - Implementation Expected
Martyn’s Law is anticipated to be fully implemented, marking a significant milestone in public safety legislation in the UK.
Sept 2024 - bill formally introduced in Parliament
The Terrorism (Protection of Premises) Bill, known as Martyn’s Law, was formally introduced in Parliament. The bill outlines requirements for venues to undertake risk assessments, provide staff with terrorism protection training, and implement measures to mitigate attacks.
October 2024 - Parliamentary Second Reading.
MPs voted to approve the Terrorism (Protection of Premises) Bill at its second reading.
The Bill will now enter its’ pre-legislative parliamentary scrutiny period before entering The House of Lords.
October 2024 - Committee stage
Line-by-line consideration and debate of the Bill.
Martyn's Law received Royal Assent on the 3rd April 2025.

What is Martyn’s Law?
Martyn’s Law will improve protective security and organisational preparedness across the UK by mandating, for the first time, those responsible for premises and events to consider the terrorist risk and how they would respond to an attack.
When will it become law
The bill passed into law on the 3rd April 2025.
How will it be enforced?
An inspection regime will be put in place by the UK Government, and the regulator will have full powers of entry into any qualifying location. Sanctions will range from a fine or permanent closure of the location to prosecution.

Martyn's Law Timeline
May 22, 2017 - Manchester Arena Bombing
Manchester Arena Bombing: A terrorist attack during an Ariana Grande concert at Manchester Arena results in 22 deaths, including Martyn Hett, and hundreds of injuries.
2018 - The Kerslake Report published
The Kerslake Report is an independent review of the emergency response to the Manchester Arena bombing.
2018 - Figen Murray’s Advocacy Begins
Figen Murray, the mother of Martyn Hett, starts campaigning for stronger security measures at public venues to prevent similar tragedies.
2019 - The Manchester Arena Inquiry
The inquiry was established to provide a thorough and transparent investigation into the events leading up to, during, and after the attack to identify what went wrong, what could have been done differently, and how future responses to similar incidents can be improved.
2019 - Martyn’s Law Concept Introduced:
Figen Murray formally introduces the idea of Martyn’s Law, advocating for mandatory security measures at venues to protect the public from terrorism. The campaign begins to gain public and political attention.
Early 2021 - Government Consultation
The UK government conducts a consultation process to gather input on the proposed Martyn’s Law, engaging with stakeholders, including venue operators, security experts, and the public.
December 2021 - Government Commitment
The UK government officially commits to introducing Martyn’s Law, incorporating it into its legislative agenda with plans to bring the law before Parliament.
2022 - Legislative Development
The government works on drafting the law, refining its details based on the consultation process, and preparing it for implementation.
February 2024 - March 2024 - Consultation Period
The Government have launched a Martyn's Law consultation to ensure the public can share their views on these proposals for the Standard Tier.
July 2024 - King Charles Speech
King Charles' speech to both houses of Parliament addressed the adoption of anti-terrorism measures; "Measures will be introduced to improve the safety and security of public venues and help keep the British public safe from terrorism - the Terrorism (Protection of Premises) Bill."
2024 - Implementation Expected
Martyn’s Law is anticipated to be fully implemented, marking a significant milestone in public safety legislation in the UK.

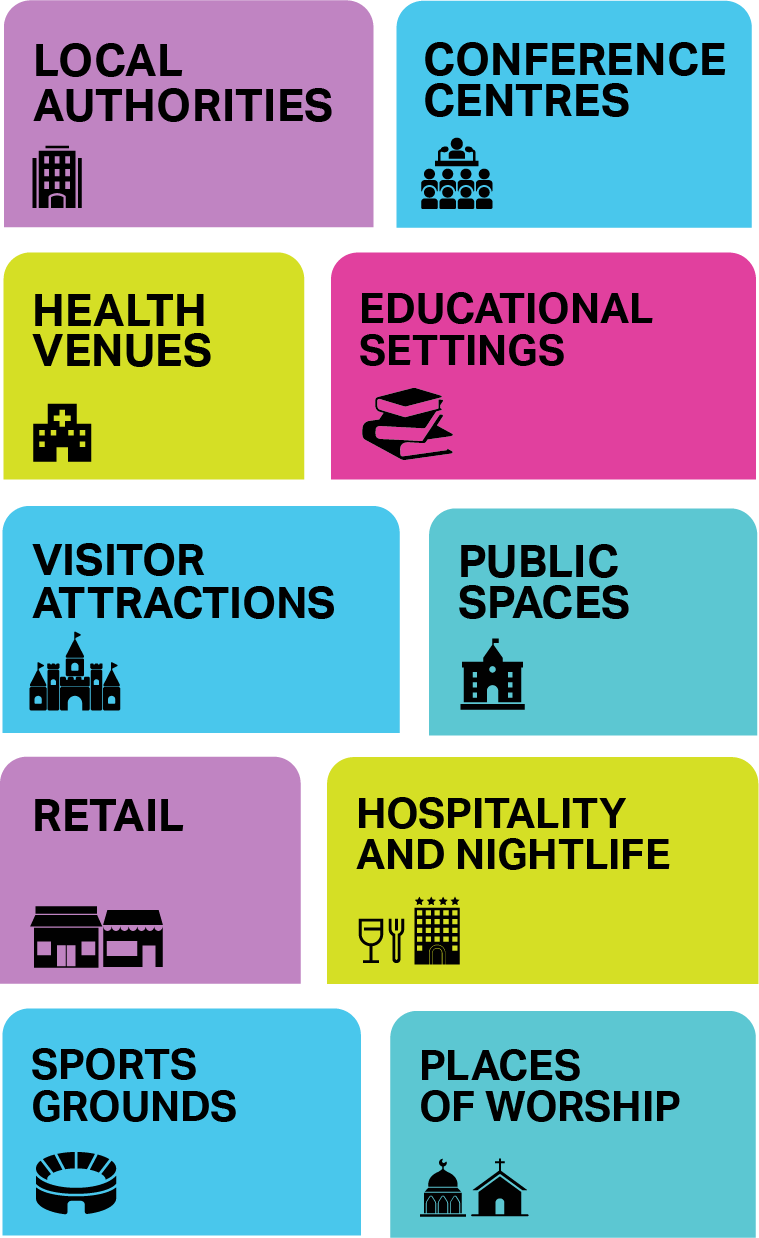
What venues are included?
The Bill will require venues to fulfil necessary but proportionate steps according to their capacity to mitigate the impact of a terrorist attack and reduce harm. The premises' duties will depend on the size of the venue. Premises and events with a capacity of 800 or above will be in the Enhanced Tier, while premises with a capacity of 200 to 799 will be in the Standard Tier.
Venues
Theatres
Cinemas
Concert halls
Arenas
Cafés
Clubs
Music venues
Pubs and bars
Restaurants
local government locations
town halls
Child care
Schools
Universities and colleges
Conference centres
Museums and galleries
Exhibition halls
Stores
Shopping centres
Stadiums and Arenas
Sports facilities
Large-scale event venues
Ice rinks
Gyms
Public sports/leisure centres
Temples
Churches
Mosques
Synagogues
Buddhist temple
Gurdwara
Hospitals
Health Centers
Large medical facilities
Museums
Art Galleries
Historic Buildings
Monuments
Holiday parks
Hotels
Public transport
Train/bus stations
Ports
Airports
Airports: Major and regional airports
Train and Bus Stations
Ports and Ferry Terminals
What venues are included?
The Bill will require certain venues to fulfil necessary but proportionate steps according to their capacity to mitigate the impact of a terrorist attack and reduce harm. The duties that premises will have will depend on the size of the venue. Premises and events with a capacity of 800 or above will be in the Enhanced Tier, while premises with a capacity of 200 to 799 will be in the Standard Tier.
Theatres
Cinemas
Concert halls
Arenas
Cafés
Clubs
Music venues
Pubs and bars
Restaurants
local government locations
town halls
Child care
Schools
Universities and colleges
Conference centres
Museums and galleries
Exhibition halls
Stores
Shopping centres
Stadiums and Arenas
Sports facilities
Large-scale event venues
Ice rinks
Gyms
Public sports/leisure centres
Temples
Churches
Mosques
Synagogues
Buddhist temple
Gurdwara
Hospitals
Health Centers
Large medical facilities
Museums
Art Galleries
Historic Buildings
Monuments
Holiday parks
Hotels
Public transport
Train/bus stations
Ports
Airports
Airports: Major and regional airports
Train and Bus Stations
Ports and Ferry Terminals

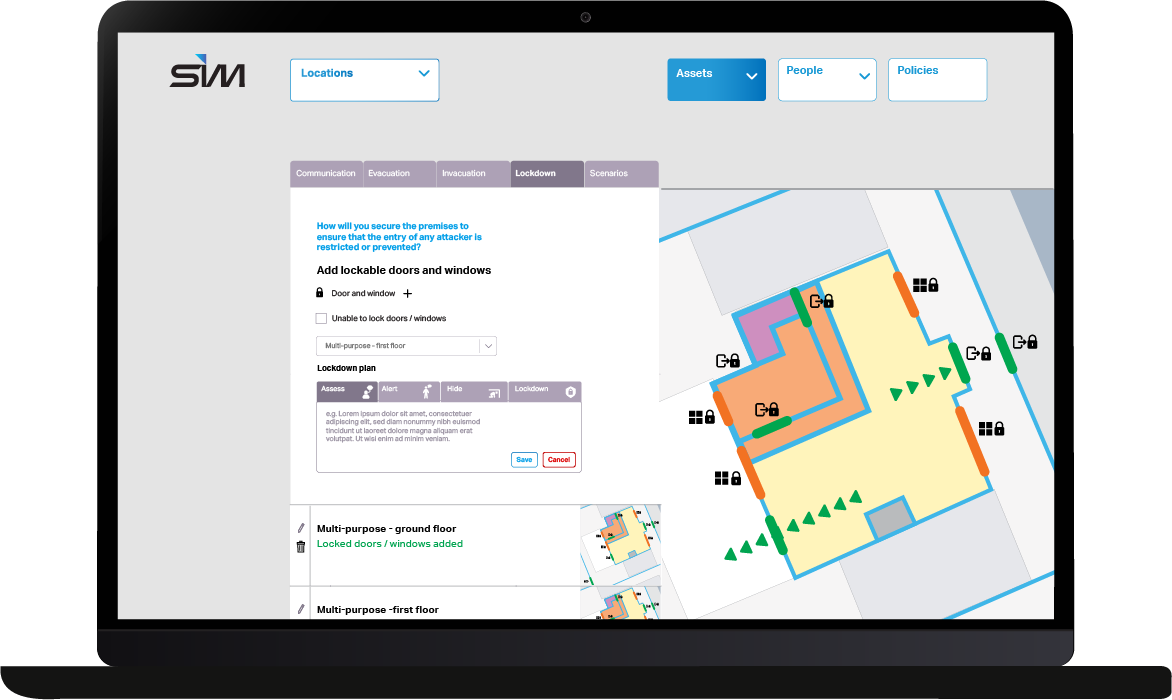
Martyn’s Law Manager to is here to help...
While it’s true you’re very unlikely to be caught up in a terrorist attack, as an employer, you are required by law to protect employees, customers, volunteers and other people visiting your sites from harm.
If you’re unfortunate enough to be part of an attack, you need to have a system in place to identify and manage the risks.


Martyn’s Law Manager to is here to help...
While it’s true you’re very unlikely to be caught up in a terrorist attack, as an employer, you are required by law to protect employees, customers, volunteers and other people visiting your sites from harm.
If you’re unfortunate enough to be part of an attack, you need to have a system in place to identify and manage the risks.
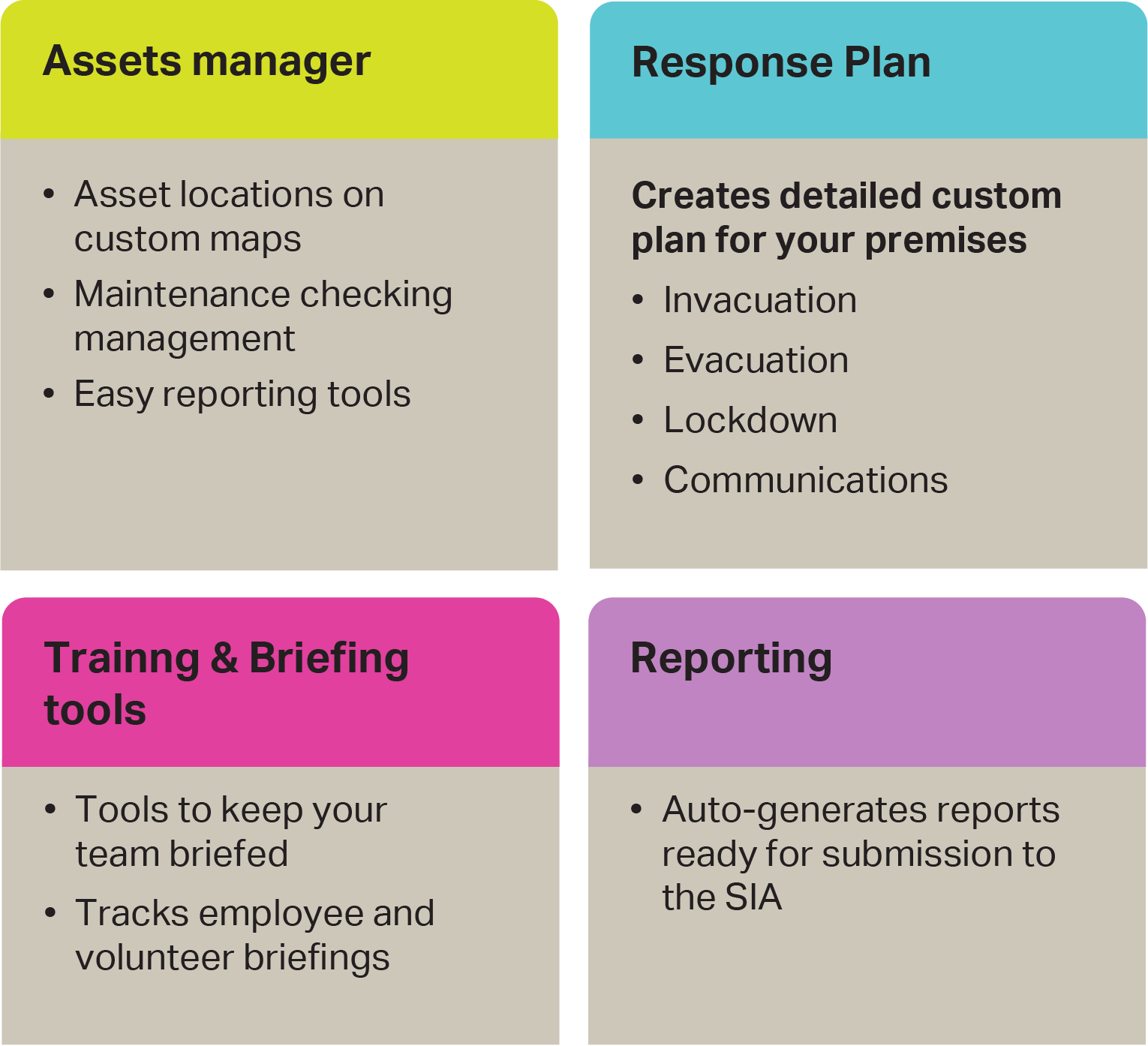
Simple step-by-step guidance
Our system digitises and automates actions recommended in the Protect UK risk assessment process. The recommended control list takes its inspiration from the operational level controls included in ISO/IEC 27001.
You get simple, sharable guidance, customised to your venue, on how to avoid incidents and also how to respond in the event of the five key incident types occurring.
Simple step-by-step guidance
Our system digitises and automates actions recommended in the Protect UK risk assessment process. The recommended control list takes its inspiration from the operational level controls included in ISO/IEC 27001.
You get simple, sharable guidance, customised to your venue, on how to avoid incidents and also how to respond in the event of the five key incident types occurring.



FAQs
Martyn’s Law, also known as the Protect Duty, is a proposed legislation in the United Kingdom aimed at enhancing public safety by requiring owners and operators of publicly accessible locations to take steps to protect people from terrorist attacks. It is named in honour of Martyn Hett, one of the victims of the 2017 Manchester Arena bombing.
Why was Martyn’s Law introduced?
Martyn’s Law was introduced in response to the growing threat of terrorism and to ensure that venues are better prepared to respond to such incidents. It aims to establish a consistent and effective approach to security across a variety of public spaces, helping to prevent future attacks and minimize their impact.
What types of locations are affected by Martyn’s Law?
The law applies to a wide range of publicly accessible locations, including but not limited to:
- Concert halls and arenas
- Shopping centres
- Public squares and parks
- Sports stadiums
- Large entertainment venues
- Places of worship
- Educational institutions
Essentially, any place where large numbers of people gather and could potentially be targeted by terrorists.
What will be the key requirements of Martyn’s Law for venue operators?
Risk Assessment: Conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats.
Mitigation Measures: Implementing appropriate and proportionate measures to reduce the risks identified, which may include physical security measures, staff training, and emergency response planning.
Training and Awareness: Ensuring that staff are adequately trained to recognize and respond to security threats.
Collaboration: Working with local authorities, emergency services, and other stakeholders to enhance overall security and preparedness.
Information Sharing: Sharing relevant security information and intelligence with appropriate authorities and other operators.
How will compliance with Martyn’s Law be monitored and enforced?
Compliance with Martyn’s Law will be monitored and enforced by designated regulatory bodies, which may include local authorities and other government agencies. These bodies will have the authority to conduct inspections, review risk assessments and mitigation plans, and take enforcement action if necessary, including issuing fines or other penalties for non-compliance.
When is Martyn’s Law expected to come into effect?
The exact timeline for the implementation of Martyn’s Law is still being determined, as it is subject to the legislative process. However, the UK government has expressed a strong commitment to moving forward with the legislation, and it is anticipated to be enacted in the near future.











SIM has a suite of digital tools ready to help keep venues, organisations, boroughs and cities safe.
Compliance
- Martyn’s Law
- Fire regulations
- Health and Safety
- Safeguarding
Incident management
- Violence
- Business continuity
- Death on property
- Fire or flood
- Power outage
- Loss of IT infrastructure
- Bomb threat
- Acts of terrorism
- Serious criminal behaviour
SIM products for all venues.
SIM has a suite of digital tools ready to help keep venues, organisations, boroughs and cities safe.
Compliance
- Martyn’s Law
- Fire regulations
- Health and Safety
- Safeguarding
Incident management
- Violence
- Business continuity
- Death on property
- Fire or flood
- Power outage
- Loss of IT infrastructure
- Bomb threat
- Acts of terrorism
- Serious criminal behaviour